Trusted Boot
Last updated February 20th, 2024
Trusted Boot is a Knox Platform feature representative of Samsung’s industry leading mobile device boot protection. Trusted Boot identifies and distinguishes unauthorized and out-of-date boot loaders before they compromise your mobile device.
If unauthorized boot components happen to load, an enterprise can trust that only validated and current components are loaded after Trusted Boot segregates authorized from unauthorized boot loaders.
Enterprises can check device integrity on demand through Knox Attestation, which reads Trusted Boot collected measurement data, along with an SE for Android enforcement setting, to form the basis of a device health verdict.
Secure lockdown on tampering
Bootloader measurements are recorded in secure TrustZone memory during device boot. At runtime, apps operating in the secure TrustZone can use these measurements to make security-critical decisions, such as whether or not to:
- Release cryptographic keys from the Knox Keystore.
- Launch the Work profile app container.
If an unauthorized or out-of-date component version is detected, a tamper fuse is set. Once the fuse is set, sensitive work apps and data within the Work container are permanently encrypted and inaccessible since the integrity of the device is no longer guaranteed or validated.
The device user can still boot the device and launch personal apps. This flexibility promotes a nice balance between consumer functions, such as smartphone calls and personal apps, and the requirement to protect enterprise data.
Building on Secure Boot
Before adopting Trusted Boot to work along with Secure Boot, Samsung devices were using Secure Boot to prevent unauthorized bootloaders and operating systems from loading during start-up. Secure Boot is implemented by each bootloader cryptographically verifying the signature of the next bootloader in sequence, using a certificate chain with its root-of-trust resident in hardware. If verification fails at any step, the boot process terminates.
While Secure Boot is effective at preventing unauthorized bootloaders, it is unable to distinguish between different authorized binary versions. For example, Secure Boot can’t distinguish between a bootloader with a known vulnerability as opposed to a later patched version, since both versions have valid signatures. Trusted Boot however was introduced to verify the same bootloader, kernel and platform build.
Knox Verified Boot (KVB)
Knox Verified Boot (KVB) is a new solution that both extends and enhances Android Verified Boot (AVB). While AVB only checks the integrity of the kernel and platform components, KVB extends those checks to also cover the earlier bootloaders. This provides a more comprehensive guarantee the device is booting using properly signed components that are all from the same build. KVB performs the same type of validations as the existing Trusted Boot mechanism, but it is able to do so before the device kernel is booted, and thus provides the same data protection guarantees earlier.
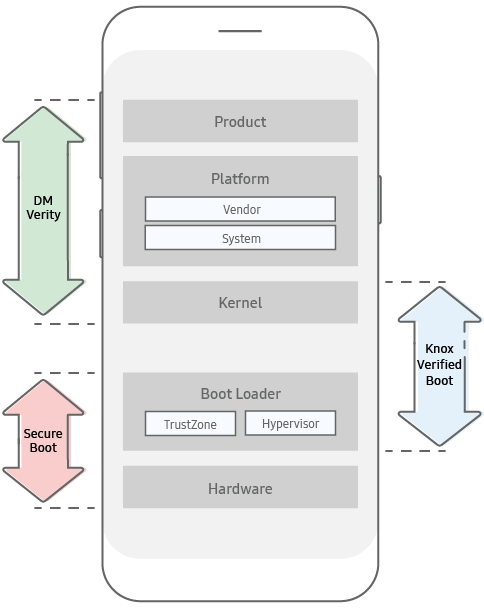
With KVB, component checks are conducted in the bootloader, and validations are made before system services are even started.
KVB is supported on Samsung S10 and above devices running the Android P operating system or late
On this page
Is this page helpful?